131929-60-7
- Product Name:Spinosad
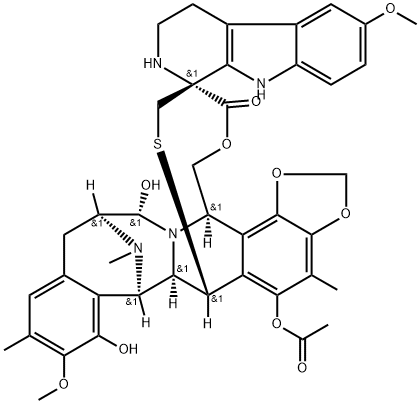
- Molecular Formula:C41H65NO10
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:731.96
Product Details:
CasNo: 131929-60-7
Molecular Formula: C41H65NO10
Appearance: White to off-white Solid
Delivery Time: 2 weeks after order
Throughput: 100KG/Month
Purity: 99%
Synonyms: (2r-(2r*,3as*,5ar*,5bs*,9s*,13s*(2r*,5s*,6r*),14r*,16as*,16br*))-ethyl; oxy-13-((5-dimethylamino)tetrahydro-6-methyl-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-9-ethyl-14-m; Spinosad A; 1H-As-indaceno(3,2-D)oxacyclododecin-7,15-dione, 2-((6-deoxy-2,3,4-tri-o-methyl-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-13-(((2R,5S,6R)-5-(dimethylamino)tetrahydro-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-9-ethyl-2,3,3A,5A,5B,6,9,10,11,12,13,14,16A,16B-tetradecahydro-14-methyl-, (2R,3as,5ar,5bs,9S,13S,14R,16as,16br)-; 1H-As-indaceno(3,2-D)oxacyclododecin-7,15-dione, 2,3,3A,5A,5B,6,9,10,11,12,13,14,16A,16B-tetradecahydro-2-((6-deoxy-2,3,4-tri-o-methyl-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-13-((5-dimethylamino)tetrahydro-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-9-ethyl-14-methyl-, (2R-(2R*,3as*,5ar*,5bs*,9S*,13S*(2R*,5S*,6R*),14R*,16as*,16br*))-; Ccris 8937
Boiling point: 801.5±65.0 °C
Density: 1.16±0.1 g/cm3
Vapor pressure: Spinosyn A: 3.2 x 10-8 Pa; Spinosyn D: 2.1 x 10-8 Pa
Pka: Spinosyn A: 8.1 (base); Spinosyn D: 7.8 (base)
Solubility: Soluble in DMSO
Water Solubility: Spinosyn A: 290 mg l-1 (pH 5); Spinosyn D: 29 mg l-1 (pH 5)
Uses:
Spinosad is a potent insecticide for crop pathogens and ectoparasite control on animals. The spinosyns have a unique mechanism of action involving disruption of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
Biological Activity:
Spinosad is an insect nicotinic acetylcholinesterase receptors (nachrs) agonist and potent insecticide. The spinosyns are a family of macrolide natural products produced by the soil microorganism saccharopolyspora spinosa. Spinosad is identified as a naturally-occurring macrocyclic lactone that is a potent insecticide.
Relevant Products
-
Apixaban
CAS:503612-47-3
-
Lurbinectedin
CAS:497871-47-3
-
Eldecalcitol
CAS:104121-92-8