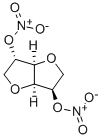
87-33-2
- Product Name:Isosorbide dinitrate
- Molecular Formula:C6H8N2O8
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:236.14
Product Details:
CasNo: 87-33-2
Molecular Formula: C6H8N2O8
Appearance: White to Off-White Solid
Delivery Time: 2 weeks after order
Throughput: 100KG/Month
Purity: 99%
Synonyms: 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-,dinitrate,d-glucito; 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-d-glucitodinitrate; 1,4:3,6-dianhydrosorbitol 2,5-dinitrate;cardis; carvanil; carvasin; [(3S,3aS,6R,6aS)-6-Nitrooxy-2,3,3a,5,6,6a-hexahydrofuro[2,3-d]furan-3-yl] nitrate
Boiling point: 378.59°C
Density: 1.7503 g/cm3
Alpha: D20 +135° (alc)
Refractive index: 1.5010
Solubility: Undiluted isosorbide dinitrate is very slightly soluble in water, very soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). The solubility of the diluted product depends on the diluent and its concentration.
Water Solubility: 549.7mg/L(25 ºC)
Air & Water Reactions: Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water.
Uses: Isosorbide dinitrate is also used in chronic cardiac insufficiency for preventing angina pectoris attacks. It is a long-lasting drug.
Antianginal; Coronary vasodilator
Definition: Isosorbide dinitrate is a nitrate ester and a glucitol derivative. It has a role as a vasodilator agent and a nitric oxide donor.
Clinical Use: Vasodilator; Prophylaxis and treatment of angina; Left ventricular failure
Relevant Products
-
Apixaban
CAS:503612-47-3
-
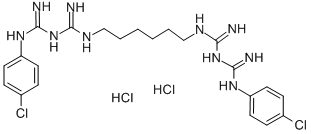
Chlorhexidine hydrochloride
CAS:3697-42-5
-
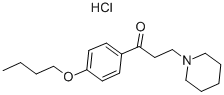
Dyclonine hydrochloride
CAS:536-43-6