52-24-4
- Product Name:Thiotepa
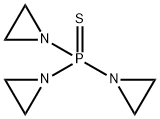
- Molecular Formula:C6H12N3PS
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:189.22
Product Details:
CasNo: 52-24-4
Molecular Formula: C6H12N3PS
Purity: 99%
Synonyms: Thioplex; Tiofosyl; Tiofosfamid; Triethylenethiophosphoramide; triaziridinylphosphinesulfide; tris(1-aziridinyl)-phosphinesulfid; tris(1-aziridinyl)phosphinesulphide; tris(ethylenimino)thiophosphate
Melting point: 54-57 ºC
Boiling point: 270.2±23.0 °C
Density: 1.50±0.1 g/cm3
Solubility: Soluble in benzene, acetone and methanol
Pka: 2.74±0.20
Form: Solid
Color: White
Water Solubility: 19g/100 mL (25 ºC)
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Description:
Thiotepa, a tertiary aziridine, is less reactive than quaternary aziridinium compounds and is classified as a weak alkylator. It is possible for the nitrogen atoms to be protonate before reacting with DNA (a positively charged aziridine is more reactive than the un-ionized aziridine), but the electron-withdrawing effect of the sulfur atom decreases the pKa to approximately six, which keeps the percentage ionized at pH 7.4 relatively low. Thiotepa undergoes oxidative desulfuration, forming an active cytotoxic metabolite known as TEPA (triethylenephosphoramide).
Uses:
This substance is listed as a known human carcinogen. It is useful for the treatment of cancers, especially cancers resistant to chemotherapy. Antineoplastic.
Indications:
Although thiotepa is chemically less reactive than the nitrogen mustards, it is thought to act by similar mechanisms. Its oral absorption is erratic. After intravenous injection, the plasma half-life is less than 2 hours. Urinary excretion accounts for 60 to 80% of eliminated drug.
Thiotepa has antitumor activity against ovarian and breast cancers and lymphomas. However, it has been largely supplanted by cyclophosphamide and other nitrogen mustards for treatment of these diseases. It is used by direct instillation into the bladder for multifocal local bladder carcinoma.
Nausea and myelosuppression are the major toxicities of thiotepa. It is not a local vesicant and has been safely injected intramuscularly and even intrathecally.
Reactivity Profile:
Triethylenethiophosphoramide polymerizes readily upon exposure to heat or moisture, especially at acidic pH.
Biochem/physiol Actions:
The unstable nitrogen-carbon groups alkylate with DNA which causes irreversible DNA damage. They stop tumor growth by crosslinking guanine nucleobases in DNA double-helix strands, directly attacking DNA. The DNA strands are unable to uncoil and separate which halts cell division.
Synthesis:
Thiotepa, tris(1-aziridinyl)phosphine sulfate (30.2.2.1), is made by reacting ethylenimine with phosphorous sulfochloride.

Relevant Products
-
Amifostine
CAS:20537-88-6
-
Melphalan hydrochloride
CAS:3223-07-2
-
Landiolol hydrochloride
CAS:144481-98-1








