2078-54-8
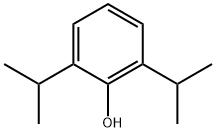
- Product Name:Propofol
- Molecular Formula:C12H18O
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:178.27
Product Details:
CasNo: 2078-54-8
Molecular Formula: C12H18O
Purity: 99%
Synonyms: 2,6-DIISOPROPYLPHENOL; 2,6-BIS(1-METHYLETHYL)PHENOL; Phenol, 2,6-diisopropyl-; Phenol,2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)-; Phenol,2,6-diisopropyl-
Melting point: 18 °C
Boiling point: 256 °C/764 mmHg
Density: 0.962 g/mL at 25 °C
Vapor pressure: 5.6 mm Hg ( 100 °C)
Fp: >230 °F
Solubility: Very slightly soluble in water, miscible with hexane and with methanol
Pka: 1.10 (H2O,t =20)(Approximate)
Form: <18°C Solid, >18°C Liquid
Color: Pale Yellow to Yellow
Water Solubility: Very slightly soluble in water
Description:
Propofol is an injectable, short-acting general anesthetic with a low incidence of side effects.
Uses:
Propofol is the active ingredient for intravenous anesthetic formulations, also has applications as an intermediate for polymers.
Definition:
Propofol is a phenol resulting from the formal substitution of the hydrogen at the 2 position of 1,3-diisopropylbenzene by a hydroxy group. It has a role as an intravenous anaesthetic, a sedative, a radical scavenger, an antiemetic and an anticonvulsant.
Biological Activity:
Intravenous general anesthetic and hypnotic with a mode of action which includes potentiation of GABA-mediated inhibitory synaptic transmission, direct activation of the GABA A receptor and inhibition of glutamate receptor mediated excitatory synaptic transmission. Also potentiates P2X 4 receptor-mediated currents in P2X 4 -HEK293 cells.
Biological Functions:
Propofol is rapidly acting, has a short recovery time, and possesses antiemetic properties. A rapid onset of anesthesia (50 seconds) is achieved, and if no other drug is administered, recovery will take place in 4 to 8 minutes.The recovery is attributed to redistribution of the drug and rapid metabolism to glucuronide and sulfate conjugates by the liver and extrahepatic tissues, such as intestine and kidney.
Rapid recovery and its antiemetic properties make propofol anesthesia very popular as an induction agent for outpatient anesthesia. Propofol can also be used to supplement inhalational anesthesia in longer procedures. Both continuous infusion of propofol for conscious sedation and with opioids for the maintenance of anesthesia for cardiac surgery are acceptable techniques.
Pharmacology:
Propofol is primarily a hypnotic drug with substantial cardiorespiratory depressant actions and with no ability to produce neuromuscular blockade. While propofol lacks analgesic properties, its use permits lower doses of opioids. Likewise, less propofol is required for adequate hypnosis when it is administered with opioids.Thus, it is said that propofol and opioids interact synergistically.
Relevant Products
-
Decanoyl/octanoyl-glycerides
CAS:65381-09-1
-
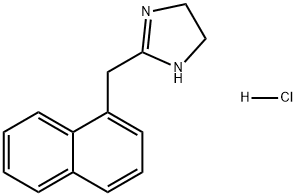
Naphazoline Hydrochloride
CAS:550-99-2
-
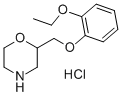
Viloxazine hydrochloride
CAS:35604-67-2