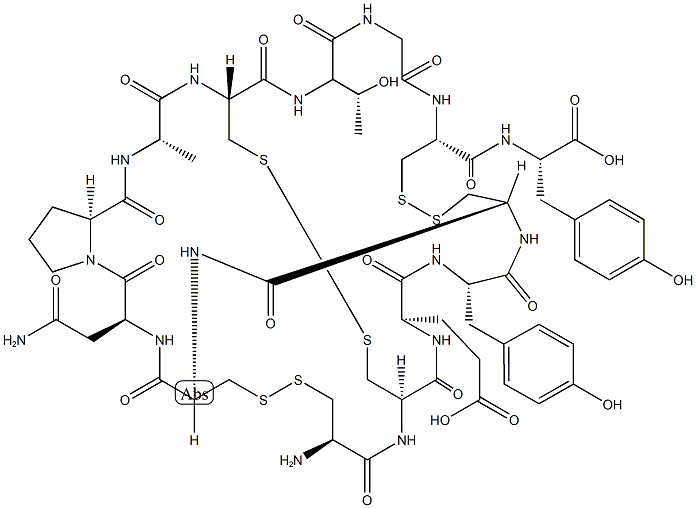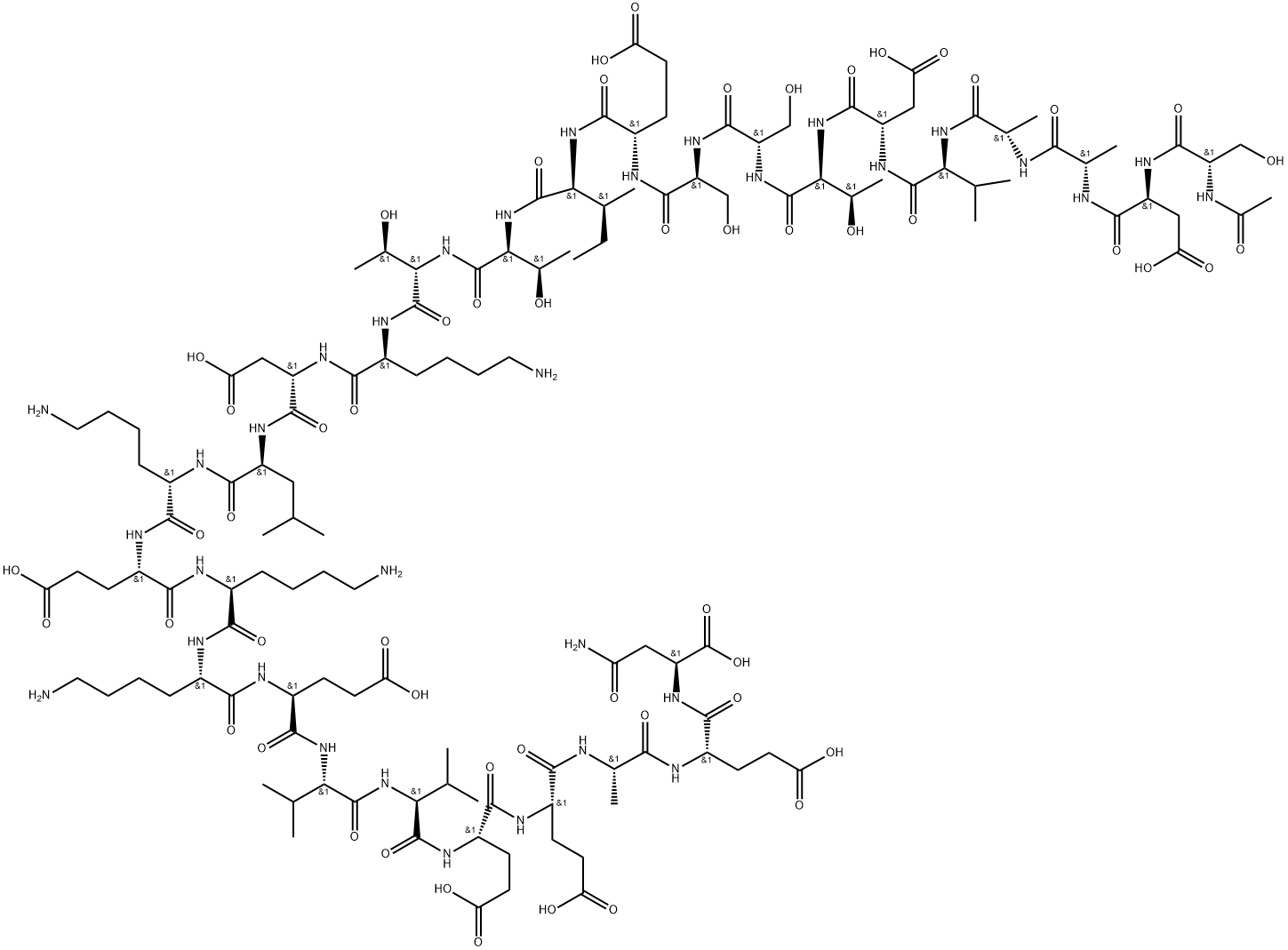
62304-98-7
- Product Name:Thymosin α1 Acetate
- Molecular Formula:C129H215N33O55
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:3108.32
Product Details:
CasNo: 62304-98-7
Molecular Formula: C129H215N33O55
Appearance: White or almost white powder or loose lump
Delivery Time: Prompt from stock
Packing: Aluminium bag
Throughput: 10KG/Month
Purity: 99%
| Description | Thymosin-α1 (T-α1), a synthetic 28-amino acid peptide with multiple biological activities primarily directed towards immune response enhancement, this drug is used for the treatment of HBV and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections, and being developed for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), hepatocellular carcinoma, AIDS and malignant melanoma. T-α1 is able to potentiate the action of cytokines and also reduce the hematological toxicity of cytotoxic drug therapy, such as cyclophosphamide, 5-fluorouracil, dacarbazine. |
| Description | Thymosin α1 is an immunomodulator peptide formed from the cleavage of prothymosin α. Thymosin α1 inhibits the growth of 5TGM1 mouse and OPM-2, LP-1, and U266 human multiple myeloma cells in vitro but not in vivo. It also increases CD3- and CD28-induced T cell proliferation in C57BL/KaLwRij splenocytes but not in allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reactions using C57BL/KaLwRij and BALB/c splenocyte co-cultures when used at a concentration of 20 μM. Thymosin α1 also inhibits the growth and migration of H1299, NL9980, and L9981 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells that express high levels of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) but not of A549 and SPC-A-1 NSCLC cells that express low PD-L1 levels. It also decreases the number of metastatic lesions in a L9981, but not an A549, NSCLC mouse xenograft model when administered at a dose of 20 mg/kg per day. Thymosin α1 (200 μg/kg) increases indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) expression and IL-10 levels and decreases IL-1β and TNF-α production in the lung in a p.Phe508del mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTRF508del/F508del) mouse model of cystic fibrosis and chronic A. fumigatus infection. |
| Uses | Zadax-in (SciClone). Thymosin alpha 1 is a peptide naturally occurring in the thymus that has long been recognized for modifying, enhancing, and restoring immune function. Immune enhancing peptide Helps prevent infections such as the common cold or the flu and diseases Reduces inflammation in the body Aids in the removal of acute or chronic infections Has antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal properties Supports the eradication of unhealthy cells Protects your cells against oxidative stress and damage Inhibits viral replication Improve symptoms associated with chronic fatigue Thymosin alpha 1 has been utilized in the treatment of immunocompromised states and malignancies, as an enhancer of vaccine response, and as a means of curbing morbidity and mortality in sepsis and numerous infections. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |
| Definition | ChEBI: Thymalfasin is a polypeptide. |
| Biological Functions | Thymalfasin is a synthetic analogue of thymosin-alpha-1, a 28-amino acid protein derived from the precursor protein prothymosin-alpha. Exhibiting a variety of immunoregulating properties, thymosin-alpha-1 induces differentiation of murine T-cell precursors and human thymocytes and the terminal differentiation of functionally immature cord blood lymphocytes and induces production of IL-2, high affinity IL-2 receptors, and B-cell growth factors by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. T-helper and cytotoxic/suppressor T-cell populations are targets of thymosin activity. Thymosin-alpha-1 has been shown to increase the efficiency of antigen presentation by macrophages and to be an endogenous modulator of alpha-thrombin activity. https://www.prospecbio.com |
| Synthesis Reference(s) | Thymosin α1 (Tα1), a 28-amino acid Nα-acetylated peptide, has a powerful general immunostimulating activity. Although biosynthesis is an attractive means of large-scale manufacture, to date, Tα1 can only be chemosynthesized because of two obstacles to its biosynthesis: the difficulties in expressing small peptides and obtaining Nα-acetylation. In this study, we describe a novel production process for Nα-acetylated Tα1 in Escherichia coli. Synthesis of Thymosin α1, a Polypeptide of the Thymus Production of Nα-acetylated thymosin α1 in Escherichia coli Synthesis of thymosin .alpha.1 |
| Clinical claims and research | Thymosin α1 (Tα1) is a 28 amino acid peptide produced by thymic epithelial cellslocated in the outer cortex and medulla of the thymus (Hirokawa et al., 1982).Invitro studies involving the use of bone marrow and progenitor cell cocultures haverevealed Tα1's capacity to stimulate thymocyte maturation (Knutsen et al.,1999).Inaddition,the administration of Tα1 in mice has resulted in notable increases inmurine thymic size and thymocyte numbers,further demonstrating Tal's abilityto enhance thymocyte growth (Beuth et al., 2000).Tα1 is likely to exert its stimula-tory effect on developing thymocytes partly by acting as an anti-apoptotic agent(Baumann et al.,1996). Interestingly,the addition of Tα1 to thymocyte andthymic epithelial cell cocultures was found to increase the production of IL-7 byepithelial cells, suggesting that the enhancing effect of Tal on thymopoiesis may bethrough the induction of IL-7 (Knutsen et al.,1999). Basic Biology and Clinical Impact of Immunosenescence |
Relevant Products
-
Apixaban
CAS:503612-47-3
-
Tirzepatide
CAS:2023788-19-2
-
Linaclotide
CAS:851199-59-2